To understand what a Real Estate Market Crash would mean in the U.S. market, we must go back to 2018. In the wake of the coronavirus pandemic, the United States experienced a significant shift in its housing market dynamics. During the pandemic, a combination of low mortgage rates and a surge in demand led to a real estate boom characterized by a fierce “race for space” and a consequential spike in home prices. However, as the landscape of 2023 unfolds, this once-thriving market is showing unmistakable signs of a slowdown. This article delves into the complex facets of the U.S. residential real estate sector, analyzing key statistics and facts that paint a picture of a market grappling with economic uncertainty, inflation, and changing consumer sentiments.
Despite the overall market cooldown, some states like Arizona and Maine witnessed remarkable home appreciation, starkly contrasting the downturns in high-value markets such as California and Washington. This dichotomy underscores the uneven impact of the market crash across different regions. Furthermore, the persistent issue of home affordability, exacerbated by stagnant income growth and escalating inflation, has put the dream of homeownership out of reach for many, particularly millennials. The Federal Reserve’s response, a gradual hike in interest rates, adds another layer of complexity, influencing both the cost of borrowing and homebuyer attitudes nationwide.
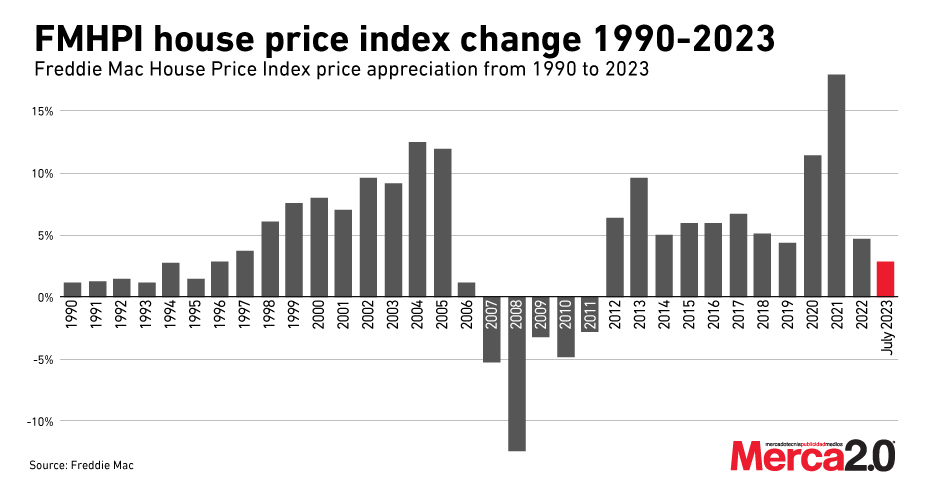
The Surge and Stabilization of Home Prices in the U.S. Real Estate Market
The trajectory of home prices in the United States over the past decade has been extraordinary. For eleven consecutive years, the nation witnessed a continuous rise in housing prices, reaching a crescendo in 2021 with an unprecedented 18 percent increase, the highest ever recorded. This remarkable growth, however, began to show signs of moderation in 2022 and sounded alarm bells of a potential Real Estate Market Crash. By July 2023, the Freddie Mac House Price Index (FMHPI) indicated a more modest year-over-year increase of 2.88 percent.
Factors Influencing Home Prices and Buyer Decisions
Understanding the real estate market dynamics requires an analysis of various influencing factors. Key among these is the relationship between household income and house prices. Ideally, a consumer is in a favorable position when their income rises concurrently with a decrease in house prices. However, recent trends have shown a disconnection between income growth and housing affordability.
Another critical element is the role of mortgage rates. These rates have been upward since 2021, impacting the monthly interest repayments for new homeowners. Higher mortgage rates tend to dampen the appeal of purchasing a home, as they increase the overall cost of borrowing. This shift has significant implications for potential homebuyers, who must now navigate a more challenging financial landscape.
As we move into 2023 and beyond, monitoring these trends and understanding their long-term implications is crucial. The real estate market remains a vital component of the U.S. economy, and its health and stability are critical indicators of broader economic well-being. Whether the market will continue to stabilize or face new challenges is a question that only time will answer.
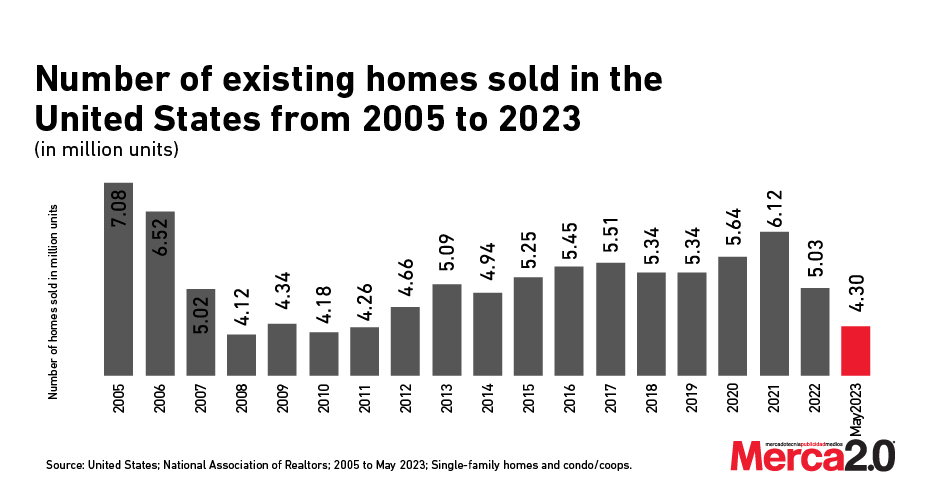
Trends in U.S. Home Sales from 1995 to 2023
The U.S. housing market has experienced significant fluctuations over the past decades, from 1995 to 2023 being particularly noteworthy. According to a report by the Statista Research Department published on October 18, 2023, these years have seen dramatic shifts in the number of housing units sold nationwide.
After a surge in 2021 that marked the highest level of home sales since 2006, the U.S. witnessed a noticeable decline in 2022. The total number of housing transactions completed in 2022 was five million, a decrease from the 6.12 million recorded in 2021. This downward trend continued into the first five months of 2023, with the annual number of single-family and condo/co-op transactions at 4.3 million as of May 2023.
Reasons Behind the Decline
Several factors contributed to the decline in home sales. The housing boom during the coronavirus pandemic had initially boosted sales, affirming the enduring appeal of homeownership in the American psyche. However, by the second half of 2022, the sentiment had shifted, with Americans across all generations agreeing that it was not an opportune time to buy a home.
The primary reasons for this change in attitude were the skyrocketing house prices and unfavorable economic conditions, making homeownership increasingly unattainable for the average buyer. The challenges included saving for a deposit, maintaining a good credit score, and securing a steady, sufficient income to be approved for a mortgage. In 2022, mortgage rates saw their most aggressive increase in history, adding to the overall cost of homeownership. As a result, only 15 percent of U.S. renters could afford to transition to homeownership, with even lower percentages in highly competitive markets like Los Angeles, CA, and Urban Honolulu, HI.
Future of Home Prices
The median sales price of existing homes was $391,500 in the third quarter of 2022, with forecasts suggesting a slight decline until the fourth quarter of 2023. The S&P/Case Shiller U.S. National Home Price Index indicated a seven-month decrease in home prices from June 2022 to January 2023, but this trend reversed in the subsequent months. New single-family homes saw an upward trend, with the median sales price soaring to about $455,000. These figures reflect the sustained demand in the housing market and highlight the significant financial commitment required for homeownership in the current economic climate.
Despite these fluctuations, home prices in many metropolitan areas are expected to grow, albeit slower. The persistent undersupply in the market due to a shortage of newly built homes to meet demand suggests that a dramatic decline in house prices is unlikely.
Real Estate Market Crash: Evolving Housing Preferences in the U.S.
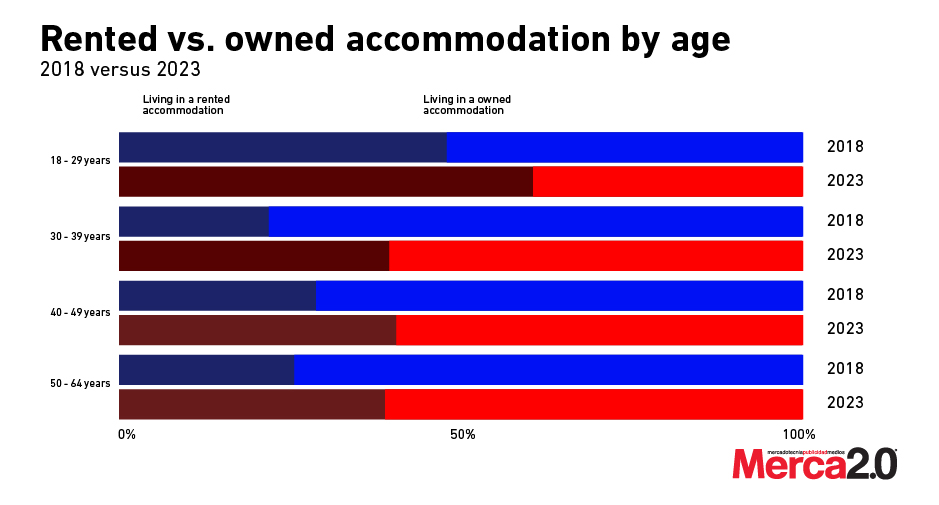
The recent Consumer Insights Survey by Statista has shed light on the shifting landscape of housing preferences in the United States and some exciting marketing trends. Analyzing data from 2018 and 2023, the survey reveals significant changes in the patterns of renting and homeownership across various age groups, indicating broader trends in the real estate market.
Young Adults Embrace Renting
In 2023, 60% of young adults aged 18-29 live in rented accommodations, a notable increase from 48% in 2018. This shift suggests that young adults are increasingly opting for rental housing, possibly due to affordability challenges, a desire for mobility, or a delay in financial readiness for homeownership. This trend could have long-term implications for the real estate market, emphasizing the need for more rental properties to accommodate this demographic.
Shifts in the 30-39 Age Bracket
The survey highlights a significant change for those aged 30-39, with 40% renting in 2023, up from 22% in 2018. This increase in renting within an age group traditionally associated with homeownership suggests that economic factors, lifestyle changes, or housing market conditions influence housing decisions. This data points to a potential reevaluation of the American Dream of homeownership among the early to mid-career population.
Middle-aged and Older Adults’ Preferences
The trend towards increased renting is also evident among middle-aged adults (40-49 years) and older adults (50-64 years). In 2023, the percentage of renters in these age groups rose to 41% and 38%, respectively, from 29% and 25% in 2018. These figures indicate a shift in housing preferences or financial capabilities, potentially driven by downsizing, economic constraints, or a desire for the flexibility associated with renting.
The data from the Consumer Insights Survey by Statista/Merca2.0 reveals a clear trend of increasing preference for rental accommodations across all age groups in the United States between 2018 and 2023. These findings underscore the need for real estate developers and policymakers to adapt to these changing preferences, potentially focusing more on developing rental properties. Understanding these evolving trends is crucial for addressing the housing needs of different demographics and planning for future real estate developments in the U.S. market.
Fluctuations in U.S. Home Sales and Pricing Dynamics (1995-2023)
The U.S. housing market, particularly from 1995 to 2023, has been a complex tapestry of economic cycles, with its most recent phase characterized by a significant slowdown and changing sales dynamics.
The Pre-Pandemic Era (1995-2019)
In the years leading up to 2020, the U.S. housing market experienced notable fluctuations. The period following the 2008 financial crisis was marked by a gradual recovery, with home prices and sales stabilizing and showing modest growth. This era was characterized by relatively balanced market conditions, with home prices largely aligning with list prices and a stable supply-demand equilibrium.
The Pandemic Surge (2020-2022)
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 catalyzed a remarkable shift in the housing market. With the implementation of low interest rates and changing lifestyle preferences due to remote work and lockdowns, there was a surge in home buying. This surge was reflected in the index for pending home sales, which spiked significantly during this period.
Simultaneously, the market faced unprecedented challenges on the supply side. Several U.S. cities reported a shortage of home inventory, exacerbated by the growing scarcity of building materials and labor. This supply constraint and robust demand led to a unique market condition where a record-high proportion of homes sold for more than their list price. In 2021 and the first half of 2022, bidding wars became commonplace, with more than half of the home sales closing above the list price.
The Market Slowdown and Price Adjustments (2022-2023)
A notable slowdown was observed as the market entered 2022 and extended into 2023. The proportion of properties selling above the list price dropped to 23 percent, a stark contrast to the fierce bidding wars of the previous years. This shift indicates a cooling down of the hyper-competitive market conditions and a gradual return to more normalized pricing strategies.
The slowdown can be attributed to several factors, including the tapering off of pandemic-driven demand, rising mortgage rates, and a general sense of economic uncertainty. Additionally, the supply issues that had plagued the market began to ease somewhat, although not entirely resolved, contributing to a more balanced housing inventory.
Assessing the Potential for a Real Estate Market Crash in 2024
As we consider the trajectory of the U.S. housing market from 1995 to 2023, culminating in the speculation of a potential crash in 2024, several key factors emerge that could shape this outcome. Analyzing past trends, current market dynamics, and emerging economic indicators provides a foundation for understanding such a crash’s likelihood and potential impact.
Real Estate Market Crash: Reflection on Recent Trends
The U.S. housing market has been on a rollercoaster ride, especially in the last few years. The pandemic-induced surge in home sales and prices, followed by a marked slowdown, has created an atmosphere of uncertainty. The shift from a seller’s market, where homes frequently sold above list price, to a more balanced or even buyer’s market in 2023 indicates a significant cooling off. While stabilizing in some aspects, this transition raises questions about the market’s future resilience.
Economic Indicators and Market Predictors
Several economic indicators are crucial in assessing the potential for a housing crash in 2024:
- Interest Rates: The Federal Reserve’s policies on interest rates, which directly impact mortgage rates, will be a determining factor. If rates continue to rise, borrowing becomes more expensive, potentially dampening homebuying activity.
- Inflation and Economic Conditions: Inflation rates and general economic health play a vital role. High inflation erodes purchasing power, while economic downturns reduce consumer confidence and spending.
- Housing Supply and Demand: The balance between supply and demand will be pivotal. An oversupply and reduced demand could lead to a price decline, while continued supply constraints might prevent a significant crash.
- Employment and Income Levels: The state of the job market and real wage growth will influence the ability of consumers to purchase homes. High unemployment or stagnant wages could negatively impact the housing market.
Potential Scenarios for 2024
Looking ahead to a Real Estate Market Crash in 2024, there are several potential scenarios:
- Moderate Correction: A scenario where the market experiences a mild correction, with a gradual price decline, is possible if the economic fundamentals remain relatively stable. This would create a neutral scenario for a Real Estate Market Crash.
- Localized Downturns: Certain regions, especially those that experienced the most significant booms, might see more pronounced downturns while others remain stable.
- Avoidance of a Full-Scale Crash: If interest rates stabilize and the economy remains robust, the market might avoid a full-scale crash, instead undergoing a period of adjustment and stabilization.