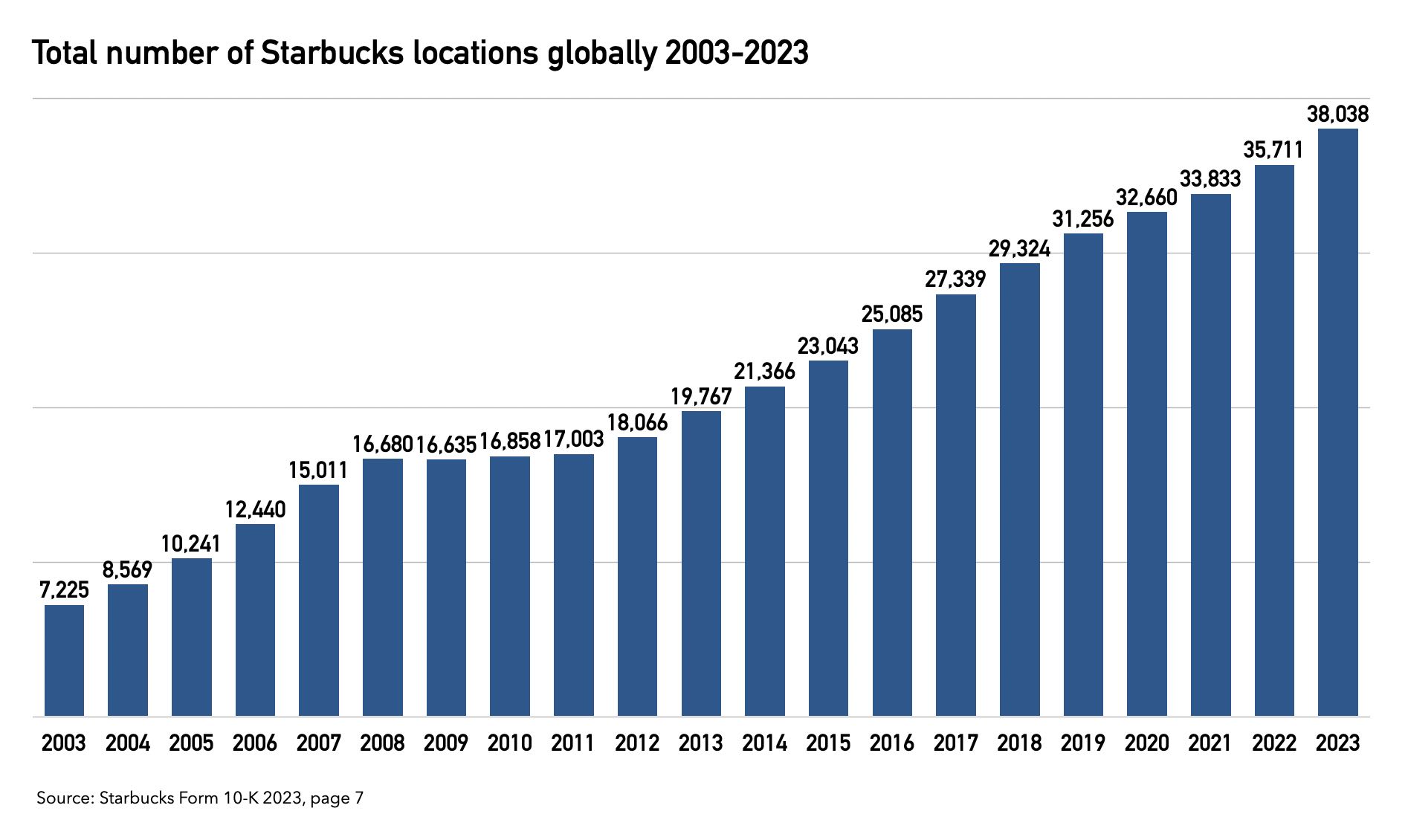
As Starbucks surpasses the 38,000-store milestone worldwide, including its various segments like Siren Retail, the question arises: Can it continue its growth trajectory? The coffee giant has experienced consistent expansion over the past decade, with a notable exception in 2009 due to the global financial crisis. This growth reflects Starbucks’ strategic emphasis on international expansion, nearly doubling its locations in the last ten years.
The United States hosts most Starbucks stores, with over 16,000 outlets, underscoring the company’s strong domestic presence. Yet, the landscape of Starbucks’ global presence changed significantly in 2018 when the number of international stores exceeded those in the U.S., highlighting the brand’s successful global expansion efforts.
Starbucks’ growth strategy includes leveraging digital technology to enhance the customer experience and operational efficiency. The introduction of the Starbucks app for pre-ordering and payment and a pilot partnership with Uber Eats for delivery illustrates the brand’s adaptation to consumer behavior trends. Especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, these digital initiatives became crucial as social distancing measures reduced in-store foot traffic, pushing Starbucks to capitalize on the booming online food delivery market, which reached approximately 923.1 billion U.S. dollars in revenue in 2023.

Furthermore, Starbucks has committed to ethical sourcing, with over 98% of its coffee verified as ethically sourced through its Coffee and Farmer Equity (C.A.F.E.) Practices. This commitment supports sustainable farming practices and aligns with consumer expectations for corporate responsibility, potentially bolstering the brand’s growth through positive consumer perception and loyalty.
However, whether Starbucks can maintain its growth trajectory is complex. Several factors could influence its expansion, including market saturation in the U.S., changing consumer preferences, and the competitive landscape. Internationally, Starbucks faces diverse challenges, including local market dynamics, regulatory environments, and cultural preferences, which require tailored strategies for successful penetration and growth.
The financial health of Starbucks, as depicted in the latest 10-K submission, shows a robust business model capable of generating significant revenue and net income. This financial stability gives Starbucks the resources to invest in new markets, store formats, and digital initiatives to drive further growth.
Moreover, Starbucks’ brand strength, customer satisfaction levels, and market position within the U.S. and globally suggest that it has a solid foundation to continue its expansion. The brand’s focus on innovation, from product offerings to digital experiences, positions it well to adapt to evolving consumer demands.
Yet, growth is not without challenges. As Starbucks continues to expand, it must navigate the complexities of global markets, including competition from international chains and local coffee shops offering unique products and experiences. The increasing consumer demand for sustainability and ethical business practices also requires Starbucks to continually evaluate and improve its supply chain, product offerings, and store operations.
Market Size
Within the context of Starbucks’ potential for growth, understanding the global coffee shop market size is crucial. As of 2022, the industry was valued at a staggering 165.7 billion U.S. dollars, according to Research and Markets, and it is projected to soar to nearly 230 billion U.S. dollars by 2030. This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2 percent, showcasing the industry’s robust current state and its promising future.
This significant market size and expected growth underline the potential to expand its global footprint further. The increasing demand for coffee shop products and services worldwide is a fertile ground for Starbucks, positioning it well to capitalize on this growing trend. As the market continues to expand, Starbucks’ strategic initiatives in product innovation, digital engagement, and international market penetration are key drivers that could enable the company to seize a larger share of this burgeoning market.
Furthermore, the growing market size indicates a rising consumer interest in coffee shop culture, including specialty coffee beverages, convenience in ordering and delivery, and the experience of enjoying coffee in a thoughtfully designed environment. With its strong brand identity and commitment to quality and sustainability, Starbucks is well-equipped to meet these evolving consumer preferences, thereby driving its growth in existing and new markets.
Starbucks marketing and advertising
In the fiscal year ending in September 2022, Starbucks significantly ramped up its marketing and advertising investments worldwide, spending 416.7 million U.S. dollars, according to its company reports. This marked a substantial increase from the 305 million dollars allocated in 2021. This strategic surge in advertising spending underscores Starbucks’ commitment to reinforcing its brand presence and engaging with consumers globally.
The Starbucks brand has an interesting approach to marketing, and advertising is multifaceted, leveraging a mix of traditional and digital media channels to reach a broad audience. The company’s advertising strategy is not just about promoting its products; it’s about storytelling, connecting with consumers’ emotions, and building a community around the coffee experience. This community-centric approach to marketing helps Starbucks to not only attract new customers but also deepen its relationship with existing ones, encouraging loyalty and frequent visits.
Moreover, Starbucks’ marketing efforts are closely tied to its broader corporate initiatives, such as ethical sourcing and sustainability. By highlighting its commitment to these values in its marketing campaigns, Starbucks not only boosts its brand image but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for responsible and transparent brands about their impact on the world.
The increase in advertising spending also reflects Starbucks’ aggressive growth strategy. As the company continues to expand its global footprint, focusing on emerging markets, it recognizes the need to invest in marketing to build brand awareness and attract customers in new territories. This is especially crucial in regions where coffee culture is not as prevalent, requiring more educational and awareness-building efforts to introduce the Starbucks experience.
Furthermore, the rise in marketing and advertising investments indicates the competitive landscape in which Starbucks operates. With an increasing number of specialty coffee shops and a growing consumer preference for local, artisanal coffee experiences, Starbucks must continually innovate and elevate its brand to maintain its market leadership. Through targeted marketing campaigns, Starbucks promotes its seasonal and specialty offerings and emphasizes the unique aspects of the Starbucks experience, from its store design to its digital ordering and loyalty programs.
There I also a negative side to the marketing push. Despite Starbucks’ expansive global presence and strategic marketing efforts, there exists a potential for consumer fatigue with the brand. This sentiment is captured poignantly in an article by Shadi Mirza on Medium titled “Dear Starbucks, I’m Tired of Your Shit.”
Consumers have a perceived dilution of the authentic coffee experience. As Starbucks has grown, some consumers, like Mirza, argue that it has increasingly prioritized efficiency and standardization over the quality and uniqueness of the coffee experience. This shift, they suggest, has led to a homogenization of the coffee culture that Starbucks once championed, making it feel less like a community-centered coffee shop and more like a fast-food chain specializing in coffee.
Starbucks Brand, growth has its limits
Firstly, the market saturation in the U.S., with over 16,000 Starbucks outlets, poses a significant challenge. The domestic market, being the largest for Starbucks, may not sustain continuous growth without diminishing returns. While innovative, the shift towards an emphasis on digital technology and delivery services may not be enough to counterbalance the effects of an oversaturated market.
Internationally, while the expansion has allowed Starbucks to surpass the number of its U.S. stores, it faces the complexities of diverse market dynamics, regulatory environments, and cultural preferences. The adaptation required for each new market involves substantial investment and risk. However, Starbucks’ aggressive growth strategy must be weighed against the potential for market overextension and the brand’s ability to maintain its quality and consumer experience standards in rapidly multiplying locations.
Moreover, the substantial increase in marketing and advertising spending reflects Starbucks’ effort to bolster its brand presence and engage consumers globally. While this underscores a commitment to growth, it also raises questions about the long-term sustainability of such aggressive marketing strategies, especially in the face of growing consumer demand for authenticity and ethical practices.