Household income in the United States varies by ethnicity, and understanding these variations is crucial for addressing income inequality. According to the US Census Bureau, the median household income for the period 2017-2021 was $69,021. However, this number varies significantly by ethnic group.
The report “Real Median Household Income by Race and Hispanic Origin” shows that the median household income for non-Hispanic White households was $72,204 in 2021, while the median household income for Black households was $47,675, and for Hispanic households was $58,947. The median household income for Asian households was $98,174, which is the highest among all racial and ethnic groups.
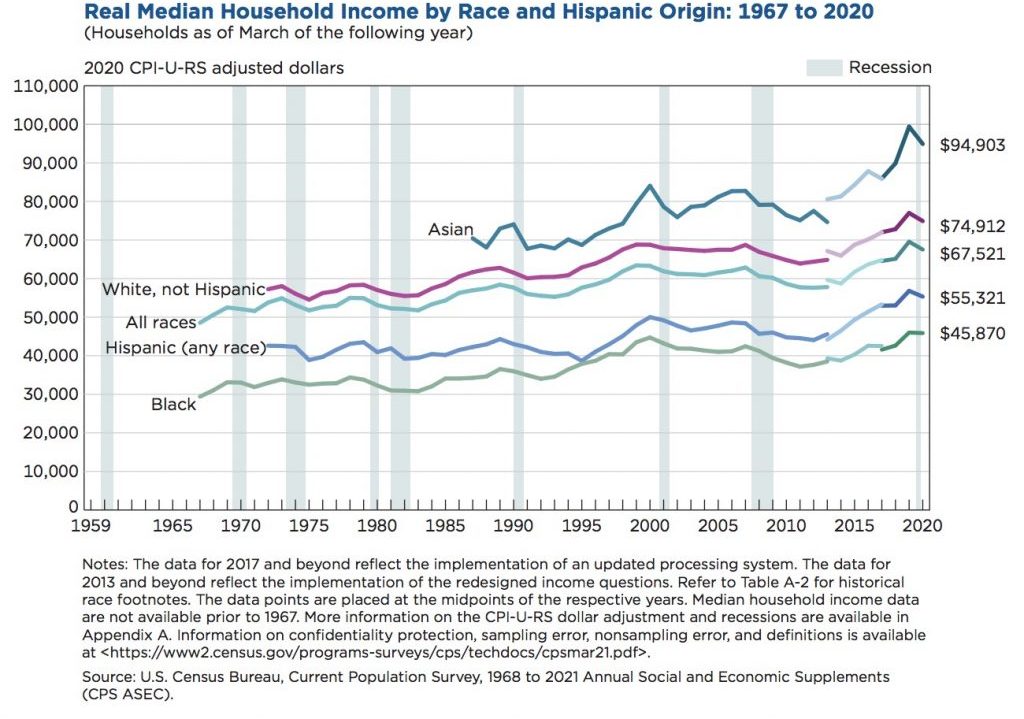
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on income and poverty in the United States. The report “Understanding Equity Through Census Bureau Data” shows that the change in median household income from 2019 to 2020 was not statistically significant for Black households, while it declined by 4.5% for Asian households. The poverty rate in 2020 was higher for the Black and Hispanic populations than for the non-Hispanic White and Asian populations.
It is important to note that household income has changed over the years. The report “Household Income by Race and Hispanic Origin” shows that real median household income in the United States increased by 2.3% between 2005-2019. Since 2008, median household income increased 14.1% for Black households, compared to 24.3% for Hispanic households, 11.1% for non-Hispanic White households, and 25.7% for Asian households.
The graph provided by Statista shows that Black Americans have consistently had the lowest median income from 1967 to 2021, while Asian Americans have had the highest.
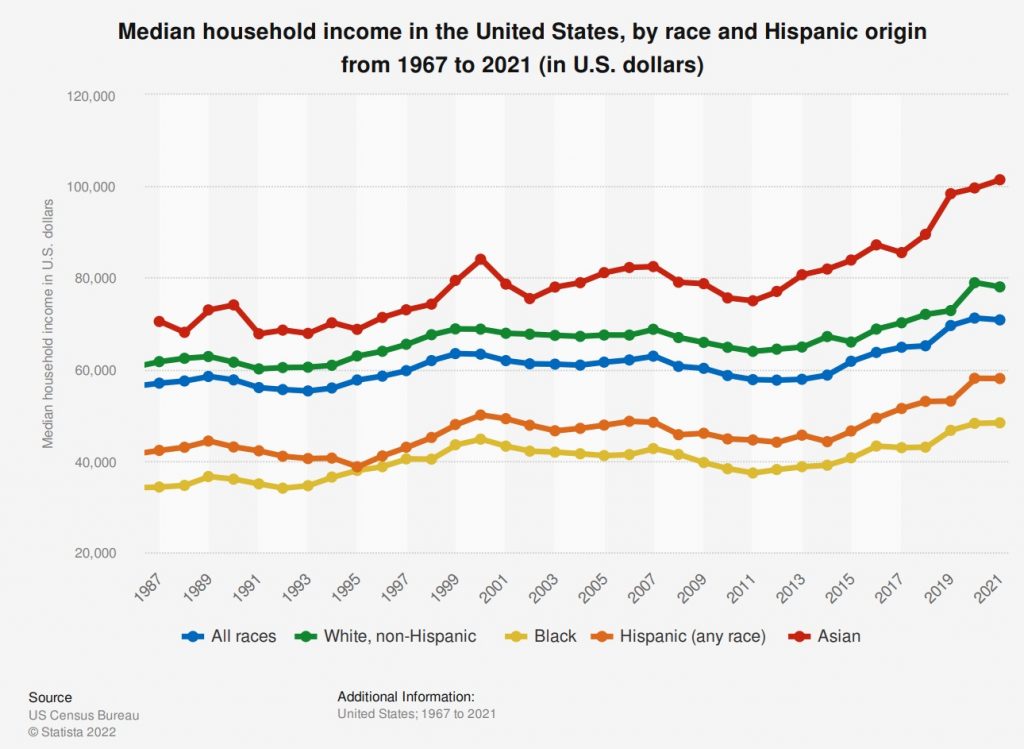
It is clear that there is a significant disparity in household income by ethnicity in the United States. It is essential to continue to study these variations and work towards policies and initiatives that address income inequality and promote economic equity.
There are significant differences in median household income across different ethnic groups in the United States. However, it is important to recognize that these disparities are complex and have a range of underlying causes. It is not productive or fair to place blame on any one particular group for these disparities.
Instead, we should focus on identifying and addressing the root causes of these disparities. This might involve looking at factors such as systemic racism, unequal access to education and employment opportunities, and discrimination in the workplace.
Furthermore, we should strive to approach these discussions with empathy and understanding, rather than blame and finger-pointing. This means recognizing the ways in which individuals from different ethnic groups may have unique challenges and experiences, and working together to create a more equitable society for all.










